|

| |

Although vibration damage to structures is usually described in non-scientific settings in terms of "cosmetic" and
"structural" types, understanding the specific kinds of damage which can occur, their
causes, their implications and how to address them is essential both to establishing and pursuing a construction vibration
damage claim. On this page, we'll give some tips, with illustrations, of how to
recognize the various types of damage. This chapter is part of the free Construction Vibration Damage Guide for Homeowners, available in part online or in full as a
free downloadable PDF, minus ads and navigation and with substantial added content. An Executive Summary is available for those in a
hurry. A broader view of its content can be found on its Introduction page, which I believe most visitors to Vibrationdamage.com should take time to read carefully. Appendix B of the CVDG, available in the CVDG Professional Edition, has a compilation of
warning signs of possible construction-related vibration damage. This should help you in searching for and identifying possible damage. Reporting and Examination of Damage
People are at least a factor of ten more sensitive to feeling vibration than buildings are to damage from it. They often feel vibrations, but do not report them until they see damage, usually later. There are very few
examples where the cracks are seen forming as the vibrations occur, even when the vibrations substantially exceed standard limits. However, even vibrations at a distance that would not get most people worried could still cause
damage to a building from the additive buildup of vibration movements, due to resonance in the building structure. Because buildings are less sensitive to vibrations than people are to perceiving it, the only real scientific
indicators of damage potential are measured PPV's and their correspondence with accepted and appropriate standards.
There is often a delay of days or months in damage reports from vibration occurrences, simply because most people don't know about damage potential from construction vibration or don't take the time to look for damage more
carefully until they see the first example of it, in their own homes or those of others. Because such delays are so common, one cannot depend on the time of reporting as indicative of the time of damage nor can one interpret that
delay as indicating that damage didn't happen prior to the report. Thus, the best sources of information about the damage and its possible causes come from documentation (photos, videos, written reports) of both the damage and the
surrounding construction, created as soon as possible after the damage is done and recognized. Preferably, the evidence is recorded while the construction is still in progress around the site.
Such contemporaneous evidence is far more reliable and attributable than an expert inspection done months or years after damage onset. Any expert examining the damage, no matter what his training, experience or education, is
handicapped by the delay between the time damage is recognized and reported and the time of his inspection visit. That delay means that the initial cracks have often extended due to continued construction and/or resolution of
vibration stresses in the structure. Of course, it is possible, and often alleged by defendants in these cases, that damage was done before or subsequent to their work around the site in question, by some other, unspecified,
cause.
Finding Damage Most people don't go through their homes with any care or regularity looking for signs of vibration-related or other damage. Early-stage vibration damage
can involve slight drywall or plaster cracking or other forms of distress for which you will have to look in order to
note it. In our experience, it is the rule, rather than the exception, that
homeowners with construction vibration damage will feel they have no damage from
the nearby construction, until they look for it with an eye to the specific and
diagnostic types of damage that are discussed below. A few small hairline cracks in drywall or plaster are not, by themselves, cause for concern about damage from nearby construction. More than ten or so readily visible damage
sites, of any size, constitute good reason to investigate further and
document carefully.
Possible "Structural Damage" Indicators
"Structural" vibration damage is best evaluated by a civil or structural
engineer having real and specific scientific knowledge of vibration damage effects, not just claimed "experience". If you make a
claim, whether or not you have to litigate it, it's a good bet that the
construction company or its insurer will want to send an engineer to assess
the house on its behalf. Since that engineer works for the opposing
side, you may or may not get full and unbiased answers, but you can express your
concerns about specific types of damage and sites to the engineer for his opinion and evaluation. Eventually, you will probably
have to bring in your own engineer or other expert in vibration damage for a second opinion.[12] In the discussion below, I include in the structural damage
category damage to home mechanical systems, which, like damage to structural members, often requires the home to be vacated for weeks or months to effect repairs.
The scientific literature, supplemented by my considerable experience with vibration damage occurrences and many discussions with engineers about vibration damage,
indicates that there are some simple signs to look for that might indicate that you
should have an engineer check for underlying
structural damage: (Click each thumbnail to view the full-sized image)
-
 Cracks
in the house slab or connected patios and driveways - These may not
constitute structural damage; but, if they are not pre-existing (i.e. present before construction start), they are
signs that should be discussed with an engineer in the context of structural
damage to the house. Cracks in tile or grout can reflect cracks in the
underlying slab. To the extent that the house slab and/or patios are
monolithic pours (connected together and poured at the same time), information in
the blasting vibration study
USBM
RI 8507 indicates that such cracks, if caused by construction, result from vibrations far in excess
of any U.S. standards.[3] Our CVDG Pro chapter, Inferring Vibration
Levels, has more
information on inferring vibration levels from damage patterns. Cracks
in the house slab or connected patios and driveways - These may not
constitute structural damage; but, if they are not pre-existing (i.e. present before construction start), they are
signs that should be discussed with an engineer in the context of structural
damage to the house. Cracks in tile or grout can reflect cracks in the
underlying slab. To the extent that the house slab and/or patios are
monolithic pours (connected together and poured at the same time), information in
the blasting vibration study
USBM
RI 8507 indicates that such cracks, if caused by construction, result from vibrations far in excess
of any U.S. standards.[3] Our CVDG Pro chapter, Inferring Vibration
Levels, has more
information on inferring vibration levels from damage patterns.
-
 Misaligned
doors and windows - Misalignment can be seen by looking at the door in
the frame. If the door doesn't show a reasonably constant spacing all the
way around between it and the frame, it has become misaligned. Some doors
and windows may become difficult or impossible to open or lock, if the misalignment is large
enough. Windows may become difficult to operate when misaligned. If you also
see diagonal drywall cracks at corners of window and door wall penetrations
(see below), these are additional signs that the house has undergone shear, possibly
due to vibration, which is causing the misalignment. Checking the door and
window frames for plumb and level, using a level, can strengthen an argument that the
house structure has shifted in response to construction vibration. Misalignment may also appear in plumbed (vertical) fixtures (TV mountings, shelving, e.g.) which are directly attached to the wall studs. Misaligned
doors and windows - Misalignment can be seen by looking at the door in
the frame. If the door doesn't show a reasonably constant spacing all the
way around between it and the frame, it has become misaligned. Some doors
and windows may become difficult or impossible to open or lock, if the misalignment is large
enough. Windows may become difficult to operate when misaligned. If you also
see diagonal drywall cracks at corners of window and door wall penetrations
(see below), these are additional signs that the house has undergone shear, possibly
due to vibration, which is causing the misalignment. Checking the door and
window frames for plumb and level, using a level, can strengthen an argument that the
house structure has shifted in response to construction vibration. Misalignment may also appear in plumbed (vertical) fixtures (TV mountings, shelving, e.g.) which are directly attached to the wall studs.
- Mechanical system problems - If you suddenly start to experience plumbing failures
underground (e.g. irrigation or waste line pipe shattered) or at the point
where the house supply connects at the slab to the incoming line from the street,
especially in the context of other vibration damage, it may be an indicator
of possible structural damage. Problems with any other lines which go
underground (heating, gas, etc.) may also indicate the possibility for
structural damage. Damage to irrigation system solenoid valves can also occur due to very large construction vibrations. If you have such mechanical system damage, there is a very good chance
that others nearby will have it, too, so keep your eye out for plumbing and heating firm trucks in your area.
- Cracks in dry wall with vertical displacements - Most cracks in
drywall are considered as "cosmetic" in nature. However, if you have cracks in
which one side of the crack is substantially higher than the other side,
this could be a sign of underlying structural damage. Also, any crack in
drywall in which the failure is not along a join between sheets, but in the
sheet itself, especially if it is jagged in appearance, may indicate a possible
underlying structural issue requiring further investigation. (photo below)
- Roof damage - Shingled roofs will usually show little sign of
damage from vibration to the underlying trusses, because the shingles can move enough with the vibration to
hide damage, if it occurs. Roof leaks are sometimes signs of otherwise invisible damage. However, tiled roofs have penetrations which are usually sealed
with concrete "cones". If these are broken, it could be a sign of structural
problems. Usually breaks in the cones result in water leaks. Leaks are also
signs of potential structural problems in buildings with shingled roofs.
Cosmetic Damage
Many houses beyond ten or fifteen years in age will have a few (less than
ten) hairline cracks along drywall seams and/or at drywall corner beads, due to slight
settling, changes in temperature and humidity, or normal aging of the drywall. Most times, the residents of the house will not even be aware that
these are present, because they are often, initially, hairline cracks which are not easy to see, unless one sets out to find
them.[8] Once people find such cracks, they can become more sensitized to them and look
for
others. The possible existence of unseen, pre-existing cracks is well-recognized, both in the
scientific literature of ground vibration damage and by contractors. For this
reason, you will almost certainly be told by those working for a contractor that your damages were all pre-existing
and that you had simply not seen them in the past.
Because limited minor cracking can occur for reasons other than construction
vibration, the timing of the damage is important in connecting it to the
construction work. On the occasion of our damage, the witnessed and videotaped construction vibration
produced over 300 immediate cracks, plus damage to concrete block property walls and a monolithic
poured concrete patio, in one day! Additional cracking
appeared later, as the job continued over strenuous objections from me and
others whose houses had been seriously damaged by the same construction. The continuation of the job led to additional damage later, thus increasing the repair cost.
When looking at your home for
"cosmetic" cracks (either before or after start of construction work), here are some locations you should check and ways to
begin to differentiate vibration cracks from settling (or aging) cracks:
 Linear
hairline drywall cracks at corner beads and at sheet joins - These are
common in both settling and vibration damage. They take on a nearly line-like appearance, as the crack is directed along the corner bead edge or sheet join. Mostly, the cause can be
differentiated only by the timing of appearance and the number of cracks
which appear in connection with construction. In my experience,
vibration-related cracks tend to be longer and more numerous than those
caused by settling. They also tend to expand with time. Because settling and vibration cracks of this sort look
so similar, documentation of the time and circumstances of their appearance
is important. Linear
hairline drywall cracks at corner beads and at sheet joins - These are
common in both settling and vibration damage. They take on a nearly line-like appearance, as the crack is directed along the corner bead edge or sheet join. Mostly, the cause can be
differentiated only by the timing of appearance and the number of cracks
which appear in connection with construction. In my experience,
vibration-related cracks tend to be longer and more numerous than those
caused by settling. They also tend to expand with time. Because settling and vibration cracks of this sort look
so similar, documentation of the time and circumstances of their appearance
is important.- Diagonal cracks at corners of wall penetrations (windows, doors,
etc.) -
 There are some characteristics of vibration cracks which
typical settling cracks rarely share. Cosmetic
drywall cracks from vibration often appear at the corners of
windows and doors, running in and roughly diagonally outward from the corners.
Corresponding cracks often manifest themselves outside around wall penetrations in rigid finishes like stucco.
These diagonal cracks are due to the house being placed in shear (i.e.
sections of the house moving in different directions or speeds with respect to one another) by
vibrations. These shearing vibrations in the home are known in the field as "racking"
motions (see Figure 13 in USBM RI 8507)[1] . They are different in nature and consequences from the so-called
"mid-wall" vibrations ("bending") which lead to pictures rattling on vibrating walls,
although racking and bending motions often occur together. Such racking cracks rarely appear house-wide in normal uniform settling and are often
indicative of vibration damage, especially when seen in multiple structures
in a given neighborhood. There are some characteristics of vibration cracks which
typical settling cracks rarely share. Cosmetic
drywall cracks from vibration often appear at the corners of
windows and doors, running in and roughly diagonally outward from the corners.
Corresponding cracks often manifest themselves outside around wall penetrations in rigid finishes like stucco.
These diagonal cracks are due to the house being placed in shear (i.e.
sections of the house moving in different directions or speeds with respect to one another) by
vibrations. These shearing vibrations in the home are known in the field as "racking"
motions (see Figure 13 in USBM RI 8507)[1] . They are different in nature and consequences from the so-called
"mid-wall" vibrations ("bending") which lead to pictures rattling on vibrating walls,
although racking and bending motions often occur together. Such racking cracks rarely appear house-wide in normal uniform settling and are often
indicative of vibration damage, especially when seen in multiple structures
in a given neighborhood.
 Drywall nail or screw "pops" - These appear as places where the
"mudding" over the screw or nail is either raised, has multiple small
radiating cracks or is missing entirely (see photo at left). If
widespread and significant in number, they also imply shear forces, likely due to vibration. Drywall nail or screw "pops" - These appear as places where the
"mudding" over the screw or nail is either raised, has multiple small
radiating cracks or is missing entirely (see photo at left). If
widespread and significant in number, they also imply shear forces, likely due to vibration. - Cracks
in drywall with vertical edge-to-edge displacements - As discussed
above, these cracks often appear in situations in which the house has been
subjected to shear, due to vibrations. The vertical displacements (i.e. with
one side of the crack substantially higher than the opposing side) are
indicative of the shear process and may signify some shifting in the frame
of the house.
- Damage
to exterior finishes - Just as vibration damages drywall, it will also
usually cause cracks in exterior rigid finishes like stucco.
 Cracks in
stucco running diagonally from wall penetrations are indicative of
vibration-induced shear, just as they are in interior drywall. In extreme cases, corresponding cracks can appear both on the interior drywall and the exterior finish. Cracks in
stucco running diagonally from wall penetrations are indicative of
vibration-induced shear, just as they are in interior drywall. In extreme cases, corresponding cracks can appear both on the interior drywall and the exterior finish.
  Cracks
in exterior property walls - Particularly in the U.S. Southwest, exterior concrete block
"tumbleweed walls" are common dividers at property lines. These, and other masonry walls, are also
damaged by extreme vibration. This damage can take the form of both cracks in
mortar or cracks in the blocks themselves. Cracks
in exterior property walls - Particularly in the U.S. Southwest, exterior concrete block
"tumbleweed walls" are common dividers at property lines. These, and other masonry walls, are also
damaged by extreme vibration. This damage can take the form of both cracks in
mortar or cracks in the blocks themselves.Cracking of concrete - Similarly, there can be cracking in monolithic (poured at the same time) concrete
slabs, driveways or patios (see at right for example of construction-caused slab cracking).
A s discussed in the
USBM
study, RI 8507, cracks in monolithic concrete, mortar or blocks can be good indicators of the intensity of the vibrations,[2] since it requires vibration
velocities
well above any standard in the U.S. to break mortar, concrete blocks or
monolithic concrete.[3],[5],[6] s discussed in the
USBM
study, RI 8507, cracks in monolithic concrete, mortar or blocks can be good indicators of the intensity of the vibrations,[2] since it requires vibration
velocities
well above any standard in the U.S. to break mortar, concrete blocks or
monolithic concrete.[3],[5],[6] The OSM also provides guidance on these matters in its
Blasting
Guidance Manual,[5],[6] - "Cracks will not normally appear in concrete
below perhaps 10.0 inches per second, a velocity that is not only far
higher than OSMRE regulations permit, but that would normally cause
undisputed and quite extensive cracks to occur to plaster, gypsumboard
and brickwork. Damage to concrete is therefore normally accompanied
not only by exceptionally high velocities, but also by other, and
obvious damage." (emphasis added)
 The OSMRE Blasting Guidance Manual provides substantial advice, very similar
to that offered here, for identifying damage and associating it with vibration
events.[4] The CVDG Pro page, Inferring Vibration Levels, has more
information on inferring vibration levels from damage patterns. The OSMRE Blasting Guidance Manual provides substantial advice, very similar
to that offered here, for identifying damage and associating it with vibration
events.[4] The CVDG Pro page, Inferring Vibration Levels, has more
information on inferring vibration levels from damage patterns.
Other Property Damage Concerns
Construction may cause damage for reasons other than vibration, per se. Breakage of gas or water mains (e.g. see video frame capture at left of a flooded street and adjacent property, resulting from a construction-broken water main)[7] can lead to
damage to property that will require
fixing. If any excavation must be done on your property to further the
construction (e.g. connecting meters to water mains), that is sometimes poorly cleaned up, if at all. Compaction of the soil caused by the construction can damage or kill nearby trees and ornamental plants. Soil compaction can
occur due to equipment-caused vibration and loading of the soil by people, equipment and materials.[11]  In-ground
PVC irrigation piping and solenoid valves can also be damaged by large vibrations. If you have damage
of any of these types, they should be included in your damage repair claim. In-ground
PVC irrigation piping and solenoid valves can also be damaged by large vibrations. If you have damage
of any of these types, they should be included in your damage repair claim.
Continuing Damage
The types of damage seen here may continue to appear for many months after
the construction ends. Most engineers advise waiting at least six months
before fixing any construction damage. The reason for this is that the
adjustment of the home to stresses placed on it by the vibrations often isn't
completed when construction or vibration ends. At right is shown a diagonal construction vibration-caused crack in drywall, beginning at the wall penetration corner at the lower right of the photo. Its length was marked by the contractor's engineer "expert" the next business day after this damage was done
by pounding on pavement with an excavator bucket. Extension of the crack over time well beyond the initial marking is clearly visible in the photo. Thus, you may continue to have newly appearing or worsening damage after
construction is finished. Such worsening of damage doesn't necessarily mean the house is experiencing damage from some new source. It may be just the slow resolution of the underlying stresses brought about by the construction
vibration. It often takes a year or more for construction damage to become reasonably stable after construction completion. Damage Age
People sometimes come home from work and find damage that they think is new, which they attribute to nearby construction. Only rarely are the damaging events or operations witnessed in conjunction with damage formation. Thus, time of damage onset is usually vital to establishing causation. It is often
"estimated" in litigation contexts by "experts", based on appearance of crack edges, using
assumptions and judgments which are scientifically questionable.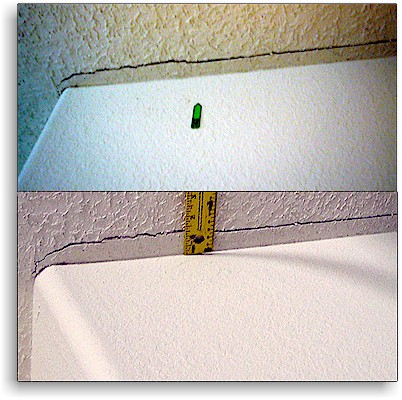 
For example, the paired photos above show the same
construction-caused drywall crack 3 days after creation (top - early in the construction job) and 139 days later (bottom - 37 days after end of the construction work at this location). There is no difference in the shared portions of the crack edges discernible to the naked eye, in spite
of the relatively long period between the photos and some extension of the crack with continued construction vibration. Thus, any meaningful deductions about the timing of this well-documented crack based on its aging with time are
impossible by mere visual inspection.[9] The hazards of estimating crack timing by simple inspection, with additional examples in different types of building materials, are discussed in more detail in the CVDG Pro's chapter, Estimating Damage Age. Documentation as close to the time of
crack formation as possible is the best way to protect
yourself against such unsupportable opinions.
Noise Issues
Construction almost invariably results in noise issues ranging from minor
discomfort, to, in extreme cases, potential health issues. While noise issues
are outside the scope of the CVDG, homeowners should be aware of their possible
contributions to nuisance and inconvenience during the construction. The FTA
Noise and Vibration Manual has extensive information on noise impacts that
homeowners may need to read. Vibration monitoring equipment has the capability to record sound as well as ground vibration, so any vibration monitoring done will often include sound data (see photo at left for an example setup
including a microphone for sound measurement).
Talking with Neighbors
If you see significant damage appear suddenly, during a construction job adjacent to or nearby your home (within hearing distance),[10] you should
inquire of your immediate neighbors whether they have noticed damage.  If
only one house is damaged, the construction contractor can blame the damage on the house or you; if several are damaged, that argument gets increasingly difficult to sustain. Chances are, your neighbors will not have looked for
damage nor will they know of any, so you will probably have to tell them what to look for in their own houses. Seeing and documenting the damage is not difficult, once you know where to look and what damage looks like. The CVDG will help you and them know for what they should search
to find. Your neighbors may also have a better idea of what was actually done during the
construction, if they are at home during normal construction working hours. Learning from neighbors and documenting damage in
their homes is a crucial issue which is discussed in more detail on our page,
Recording Damage. If
only one house is damaged, the construction contractor can blame the damage on the house or you; if several are damaged, that argument gets increasingly difficult to sustain. Chances are, your neighbors will not have looked for
damage nor will they know of any, so you will probably have to tell them what to look for in their own houses. Seeing and documenting the damage is not difficult, once you know where to look and what damage looks like. The CVDG will help you and them know for what they should search
to find. Your neighbors may also have a better idea of what was actually done during the
construction, if they are at home during normal construction working hours. Learning from neighbors and documenting damage in
their homes is a crucial issue which is discussed in more detail on our page,
Recording Damage.
This is, by no means, an exhaustive listing of all the kinds of vibration
damage which can occur. Instead, I suggest it as a starting point for those who
may feel that they have construction vibration damage and want to know what
they might look to find.
| [1] Structure Response and Damage Produced by Ground Vibration From Surface Mine Blasting, D. E. Siskind, M. S. Stagg, J. W. Kopp, and C. H. Dowding, United States Bureau of
Mines Report of Investigations 8507 (USBM RI 8507), 1980, p. 18
↩ [2] Ibid., p. 44
↩
[3] Ibid., p. 45
↩
[4] OSMRE Blasting Guidance Manual, Michael F. Rosenthal and Gregory L. Morlock, Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement, United States
Department of the Interior, 1987, pp. 121-122
↩
[5] Ibid., p. 121
↩
[6] "When major, structural damage, such as the collapse of brickwork,
extensive and serious cracking threatening structural integrity, or
concrete cracking is found (apart from the small drying-out or
temperature cracks to be found in virtually all concrete) then either
the ground motion exceeded 3 or 4 inches per second, or some other
reason exists for the damage." Ibid, p. 112
↩
[7] The contractor who created the flooded street shown in the photo, by breaking a water main, broke another water line in a different project, literally in front of the author. This occurred on January 3, 2017 a few blocks away, in which the same
contractor was performing a water main replacement and road reconstruction, very similar to the job referenced several times in the CVDG. The author documented the ongoing break, which was confined within a large, deep
hole dug to access the line, with a cell phone camera.
↩
[8] Cracks in drywall become more difficult to see under conditions of high humidity. The humidity is absorbed by the drywall. It swells slightly, closing the cracks. For this reason, it is often best to look for cracking
in the winter, when the humidity in most homes tends to be lower. You will still be able to see cracks in typically less humid winter conditions, but they will be narrower and harder
to see without intentional searching.
↩
[9] Viewing this well-documented crack, plaintiffs' experts said, correctly, that it was recent and caused by construction. Defendants' experts said that it was old and pre-existing. Neither conclusion was scientifically justifiable
based on inspection of the crack alone.
↩
[10] Effective distances for construction vibration given throughout the CVDG are guidelines only, as both sound and ground vibration can travel differently in materials and environments. These approximations are given for
those who don't have seismographic data on the vibrations available to them. See Vibration and Distance in the CVDG for much more on how vibration decreases with distance.
↩
[11] A Guide to Preventing Soil Compaction During Construction, Arnold M. Brodbeck, William J. Rowe, Francisco J. Arriaga, Alabama Cooperative Extension System, 2013
↩ [12] It has been my experience in dealing with many vibration damage cases around the world that real expertise is usually only sought 2-4 years after the appearance of the damage, often as
a civil case nears trial. Damage which is so old is practically impossible to attribute with certainty to construction, because the damage is both old and poorly documented at the time of the construction. A true expert should
examine and document damage as close to the time of the damage as possible and, in any event, no more than six months after construction has ended.
↩ |
|
  This is a chapter from the Construction
Vibration Damage Guide for Homeowners (CVDG), a 100+ page free
book with over 300 color photos, diagrams and other illustrations.
It is available at
https://vibrationdamage.com as a series of web pages or in full,
web navigation and ad-free,
as a downloadable PDF e-book, with
additional content not available on the web. The free
version of the CVDG is licensed to homeowners and others for
personal, at-home use only. A Professional Edition (CVDG Pro), licensed
for business use and with over three times as much content, can be ordered from our
Order the CVDG Pro page, usually with same-day delivery. You can comment about this page or ask
questions of the author, Dr. John M. Zeigler, by using our Visitor Comment
form. This is a chapter from the Construction
Vibration Damage Guide for Homeowners (CVDG), a 100+ page free
book with over 300 color photos, diagrams and other illustrations.
It is available at
https://vibrationdamage.com as a series of web pages or in full,
web navigation and ad-free,
as a downloadable PDF e-book, with
additional content not available on the web. The free
version of the CVDG is licensed to homeowners and others for
personal, at-home use only. A Professional Edition (CVDG Pro), licensed
for business use and with over three times as much content, can be ordered from our
Order the CVDG Pro page, usually with same-day delivery. You can comment about this page or ask
questions of the author, Dr. John M. Zeigler, by using our Visitor Comment
form.  If you would like to discuss vibration damage issues and view additional content not found in the CVDG, Join
us on Facebook. Please Like us while you're there. If you would like to discuss vibration damage issues and view additional content not found in the CVDG, Join
us on Facebook. Please Like us while you're there. |
| |
|